JOGL 2 Polygon texture mapping
|
This post was updated on .
This is how I set up my project in eclipse Helios:
 This is the texture I'm using. I pasted it here in case you want to use it:  This is the problem: 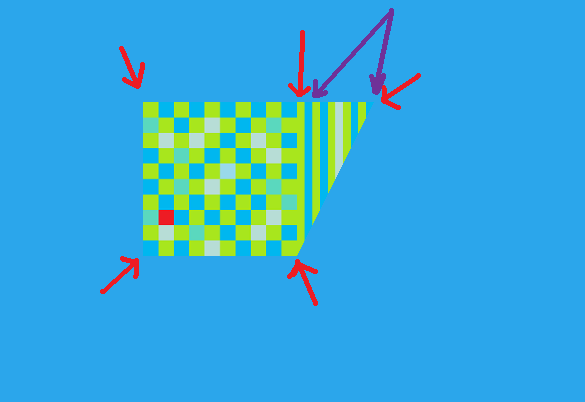 package pixelapp.texturedpolygon; import java.awt.GraphicsDevice; import java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.ByteOrder; import java.nio.FloatBuffer; import javax.media.opengl.GL; import javax.media.opengl.GL2; import javax.media.opengl.GLAutoDrawable; import javax.media.opengl.GLCapabilities; import javax.media.opengl.GLEventListener; import javax.media.opengl.GLProfile; import javax.media.opengl.awt.GLCanvas; import javax.swing.JFrame; import com.jogamp.opengl.util.FPSAnimator; import com.jogamp.opengl.util.texture.Texture; import com.jogamp.opengl.util.texture.TextureCoords; import com.jogamp.opengl.util.texture.TextureIO; /** * @author Main * */ public class TexturedPolygon implements GLEventListener { private Texture tex; private String file = "platform.png"; private String folder = "pixelapp/texturedpolygon/images/"; private JFrame myFrame; // Create JFrame object. private ClassLoader cl; // To calculate textures private final int SQUARE_VERT = 4; private float one = 1; private int cubeAcc = 0; private final int ZERO = 0; private int acc = ZERO; // Accumulator // Display private int NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY = 1; private final int MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY = 1; private FloatBuffer[] mVertexBufferDisplay = new FloatBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private FloatBuffer[] mColorBufferDisplay = new FloatBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private ByteBuffer[] mIndexBufferDisplay = new ByteBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private FloatBuffer[] mTexBufferDisplay = new FloatBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private ByteBuffer[] vbbDisplay = new ByteBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private ByteBuffer[] cbbDisplay = new ByteBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private ByteBuffer[] tbbDisplay = new ByteBuffer[MAX_NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY]; private float[] cubeFillerVDisplay = { 1f, 1f, 0f, 1f, -1, 0f, -1f, -1f, 0f, -1f, 1f, 0f, 2f, 1f, 0f, }; private float[] cubeFillerCDisplay = { one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one, one,}; private byte[] cubeFillerIDisplay = { 0, 3, 2, 0, 2, 1, 0, 1, 4 }; public TexturedPolygon() { // Set the title of the Frame. myFrame = new JFrame("TexturedPolygon"); // Close program on Finish. myFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); // Eliminates the windows frames look. myFrame.setUndecorated(true); GLProfile glp = GLProfile.getDefault(); GLCapabilities caps = new GLCapabilities(glp); GLCanvas miCanvas = new GLCanvas(caps); // Indicate Canvas to detect the events of OpenGL in this Class. miCanvas.addGLEventListener(this); // Insert Canvas in the Frame. myFrame.add(miCanvas); // Size of the window myFrame.setSize(600, 600); // Make visible the object of most weight myFrame.setVisible(true); // Renders continuously JOGL2. FPSAnimator animator = new FPSAnimator(miCanvas, 30); animator.add(miCanvas); animator.start(); // Get current classloader cl = this.getClass().getClassLoader(); /** Full Screen Mode */ GraphicsEnvironment env = GraphicsEnvironment. getLocalGraphicsEnvironment(); GraphicsDevice device = env.getDefaultScreenDevice(); device.setFullScreenWindow(myFrame); // Display // Buffers to be passed to gl*Pointer() functions // must be direct, i.e., they must be placed on the // native heap where the garbage collector cannot // move them. // // Buffers with multi-byte datatypes (e.g., short, int, float) // must have their byte order set to native order for (cubeAcc = ZERO; cubeAcc < NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY; cubeAcc++) { vbbDisplay[cubeAcc] = ByteBuffer .allocateDirect(cubeFillerVDisplay.length * 4); vbbDisplay[cubeAcc].order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); mVertexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc] = vbbDisplay[cubeAcc].asFloatBuffer(); mVertexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].put(cubeFillerVDisplay); mVertexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].position(0); } for (cubeAcc = ZERO; cubeAcc < NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY; cubeAcc++) { cbbDisplay[cubeAcc] = ByteBuffer .allocateDirect(cubeFillerCDisplay.length * 4); cbbDisplay[cubeAcc].order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); mColorBufferDisplay[cubeAcc] = cbbDisplay[cubeAcc].asFloatBuffer(); mColorBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].put(cubeFillerCDisplay); mColorBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].position(0); } for (cubeAcc = ZERO; cubeAcc < NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY; cubeAcc++) { mIndexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc] = ByteBuffer .allocateDirect(cubeFillerIDisplay.length); mIndexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].put(cubeFillerIDisplay); mIndexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc].position(0); } for (cubeAcc = ZERO; cubeAcc < NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY; cubeAcc++) { tbbDisplay[cubeAcc] = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(SQUARE_VERT * 2 * 4); tbbDisplay[cubeAcc].order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); mTexBufferDisplay[cubeAcc] = tbbDisplay[cubeAcc].asFloatBuffer(); } } /** Called by the drawable immediately after the OpenGL context is * initialized for the first time. Can be used to perform one-time OpenGL * initialization such as setup of lights and display lists. * @param gLDrawable The GLAutoDrawable object. */ public void init(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); // Initialize the variable GL // >> gl.glClearDepth(1.0f); // Set depth's clear-value to farthest gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_DEPTH_TEST); // Enables depth-buffer for hidden // surface removal gl.glDepthFunc(GL2.GL_LEQUAL); // The type of depth testing to do gl.glHint(GL2.GL_PERSPECTIVE_CORRECTION_HINT, GL2.GL_NICEST); // nice perspective view, avoid texture distortion. gl.glShadeModel(GL2.GL_SMOOTH); // Enable smooth shading of color gl.glDisable(GL2.GL_DITHER); // Disable dithering for better performance // sky color background gl.glClearColor(0.17f, 0.65f, 0.92f, 0.0f); loadTexture(file, gl); // for the billboard } private void loadTexture(String fnm, GL2 gl) { String fileName = folder + fnm; tex = null; try { tex = TextureIO.newTexture( cl.getResource(fileName), false, null); tex.setTexParameteri(gl, GL2.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL2.GL_NEAREST); tex.setTexParameteri(gl, GL.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL.GL_NEAREST); } catch(Exception e) { System.out.println("Error loading texture " + fileName); } } // end of loadTexture() public void display(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); // Initialize the variable GL /* * By default, OpenGL enables features that improve quality but reduce * performance. One might want to tweak that especially on software * renderer. */ gl.glDisable(GL2.GL_DITHER); // >> gl.glTexEnvf(GL2.GL_TEXTURE_ENV, GL2.GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL2.GL_MODULATE); /* * Usually, the first thing one might want to do is to clear the screen. * The most efficient way of doing this is to use glClear(). */ gl.glClear(GL2.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL2.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT); /* * Now we're ready to draw some 3D objects */ gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_MODELVIEW); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -5.2f); gl.glEnableClientState(GL2.GL_VERTEX_ARRAY); gl.glEnableClientState(GL2.GL_COLOR_ARRAY); gl.glEnableClientState(GL2.GL_TEXTURE_COORD_ARRAY); TextureCoords tc = tex.getImageTexCoords(); // Display mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(0); // x or s mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(1); // y or t mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(1); // x or s mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(1); // y or t mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(1); // x or s mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(0); // y or t mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(0); // x or s mTexBufferDisplay[0].put(0); // y or t mTexBufferDisplay[0].position(0); gl.glActiveTexture(GL2.GL_TEXTURE0); gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_TEXTURE_2D); // do not draw the transparent parts of the texture gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_BLEND); gl.glBlendFunc(GL2.GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL2.GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA); // don't show source alpha parts in the destination // determine which areas of the polygon are to be rendered gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_ALPHA_TEST); gl.glAlphaFunc(GL2.GL_GREATER, 0); // only render if alpha > 0 // Display for (acc = ZERO; acc < NUM_CUBES_DISPLAY; acc++) { tex.bind(gl); tex.setTexParameterf(gl, GL2.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL2.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); tex.setTexParameterf(gl, GL2.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL2.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); gl.glPushMatrix(); gl.glVertexPointer(3, GL2.GL_FLOAT, 0, mVertexBufferDisplay[acc]); gl.glEnable(GL2.GL_TEXTURE_2D); gl.glColorPointer(4, GL2.GL_FLOAT, 0, mColorBufferDisplay[acc]); gl.glTexCoordPointer(2, GL2.GL_FLOAT, 0, mTexBufferDisplay[0]); gl.glDrawElements(GL2.GL_TRIANGLES, cubeFillerIDisplay.length, GL2.GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, mIndexBufferDisplay[acc]); gl.glPopMatrix(); } } public void reshape(GLAutoDrawable drawable, int x, int y, int width, int height) { GL2 gl = drawable.getGL().getGL2(); // Initialize the variable GL if (height == 0) { height = 1; // to avoid division by 0 in aspect ratio below } float ratio = (float) width / height; gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height); /* * Set our projection matrix. This doesn't have to be done each time we * draw, but usually a new projection needs to be set when the viewport * is resized. */ gl.glMatrixMode(GL2.GL_PROJECTION); gl.glLoadIdentity(); gl.glFrustum(-ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 1, 236); } public static void main(String[] args) { new TexturedPolygon(); } public void dispose(GLAutoDrawable drawable) { } } ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- The red arrows indicate that there are 5 vertexes in this poligon (I want 5, not 4). The two purple arrows indicate to what position the texture should be extended. In other words the texture should be touching the vertex to the rightmost of the polygon. As you can see the left purple arrow points where the texture ends and then repeats it self. However I want only one texture that doesn't repeat it self to cover the entire polygon. Requirements: I can only use triangles (quads are not allowed, because of the platform they will run on). I can not use Opengl GLU in any way, because of the platform this will run on. The texture coordinates should not use methods such as put(texturecoordinate.right()) or put(texturecoordinate.left()). They should be numbers, like put(0) or put(1). Problem: I would like to map this texture in the entire (5 vertex) polygon. How do I do this? I think this is called UV mapping, I'm not really sure. I hope the pictures are all self explanatory. Please try the code for yourselves. It is very short anyways. Moreover; I'm able to texture-map a triangle or a square with the use of GL.TRIANGLES but I don't know how to map polygons. Any ideas? |
«
Return to jogl
|
1 view|%1 views
| Free forum by Nabble | Edit this page |

